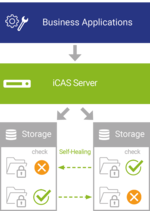
During the retention period of archived data, its integrity must be ensured in order to minimize business risks and meet various requirements (laws, compliance, internal requirements). The most common causes of data loss and unintentional data modification include data corruption, hardware mirroring limitations, accidental deletion and data migrations.
Silent data corruption
Silent data corruption is the random changing of bit states on the storage medium without external influence. This can falsify archive data and make it unreadable. The causes of this "tilting" of individual bits include aging of the media and chemical or electro-magnetic processes.
Limitation of hardware mirroring and reorganization of data
In hardware-based archive systems, replicating data at the storage level carries the risk of transferring logical errors to the target system. Hardware-based archive systems sometimes employ RAID configurations that organize multiple physical mass storages. These can cause unintentional data corruption: The more full a storage is, the more frequently data is reorganized. This increases the probability that certain data has already been written - but the associated parity information has not yet been written. If an undesired event occurs at this moment - e.g. a short-term inaccessibility of the write cache - data loss is imminent.
Data migrations
During the archiving period, data often has to be migrated several times. This involves transferring data from one system to another. This moving can result in unintentional transfer errors, which can lead to damage or loss of sensitive or critical data. For example, content-related and important meta-information such as retention period, timestamps or IDs can be lost.